Effects of Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution on Intraocular Pressure after Phacoemulsification Surgery
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad2959Keywords:
Bromfenac, Cataract, Goldman Applanation Tonometry, Intraocular Pressure, PhacoemulsificationAbstract
Background: Cataract surgery is one of the commonest surgeries. Changes in intraocular pressure (IOP) might occur after surgery and some post-operative medications might affect it.
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of the non–steroidal anti–inflammatory drug Bromfenac 0.09% ophthalmic solution on intraocular pressure after phacoemulsification and to report any side effects of the drug.
Method: It was a prospective study done at Jenna ophthalmic center, Baghdad- Iraq from May 2023 to January 2024 involving adult patients with cataract prepared for phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation. The patients were divided into two groups: Group I: received 0.09% Bromfenac ophthalmic solution twice daily in addition to Moxifloxacin 0.5% ophthalmic drops every 6 hours and Dexamethasone phosphate 0.1% ophthalmic drops every 4-6 hours post-operatively. Group II: received only Moxifloxacin 0.5% every 6 hours and Dexamethasone phosphate 0.1% ophthalmic drops every 4-6 hours without the administration of Bromfenac 0.09% ophthalmic drops post-operatively. The intraocular pressure was measured pre-operatively and 6 weeks post-operatively by Goldman applanation tonometry.
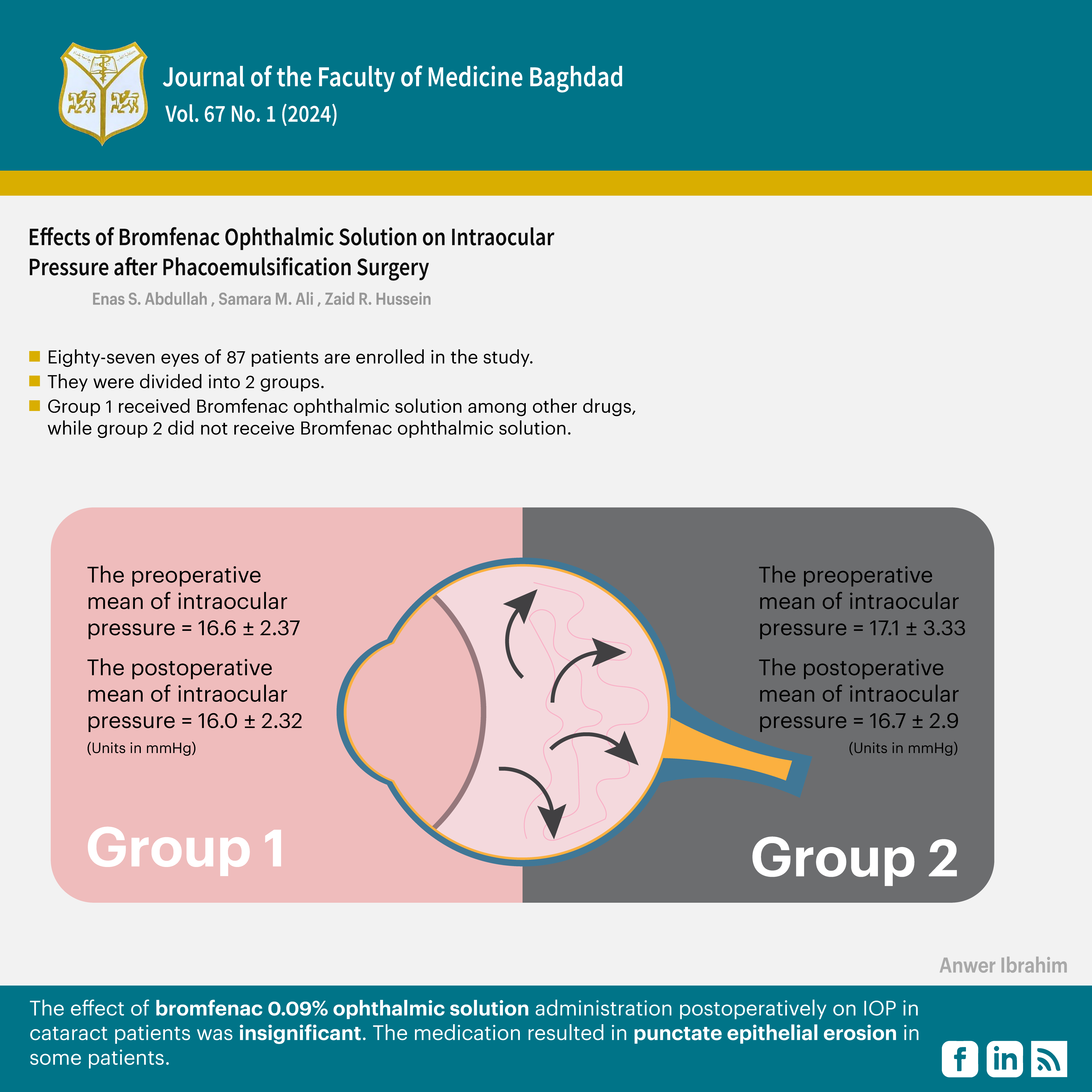
Results: Eighty-seven eyes of 87 patients are enrolled in the study. The preoperative mean of intraocular pressure in group I and group II were 16.6 ± 2.37 mmHg, and 17.1 ± 3.33 mmHg respectively (not significantly different), while the postoperative mean of intraocular pressure in group I and group II, were 16.0 ± 2.32 mmHg and 16.7 ± 2.9 mmHg respectively. There were no significant changes in IOP post-operatively in either group, and the only side effect reported was punctate epithelial corneal erosion in five patients in group I.
Conclusion: The effect of Bromfenac 0.09% ophthalmic solution administration postoperatively on IOP in cataract patients was insignificant. The medication resulted in punctate epithelial erosion in some patients.
Received: Oct. 2024
Revised: Dec. 2024
Accepted: Oct. 2024
Published: April 2025
Downloads
References
1. He L, Cui Y, Tang X, He S, Yao X, Huang Q, et al. Changes in visual function and quality of life in patients with senile cataract following phacoemulsification. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(6):3802-9. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-20-1709.
2. Narayan A, Evans JR, O'Brart D, Bunce C, Gore DM, Day AC. Laser‐assisted cataract surgery versus standard ultrasound phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2023(6). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010735.pub3.
3. Pardasani R, Lohiya S. Study of Changes in Corneal Thickness and Corneal Endothelial Cell Density after Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci.2021;10(12):866-73. https://doi.org/10.14260/jemds/2021/187.
4. Abood ZB, Kareem AA. Changes of Anterior Chamber Biometry and Relationship to Intraocular Pressure Changes after Phacoemulsification Surgery in Non-Glaucomatous Eyes. IPMJ. 2023;22(2).
5. Hashemi H, Pakzad R, Yekta A, Aghamirsalim M, Pakbin M, Ramin S, et al. Global and regional prevalence of age-related cataract: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Eye. 2020;34(8):1357-70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-020-0806-3.
6. Baek SU, Kwon S, Park IW, Suh W. Effect of phacoemulsification on intraocular pressure in healthy subjects and glaucoma patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(6). https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e47.
7. Matloub SY. The effect of topical administration of sildenafil in acute ocular hypertension model in rabbits. J Fac Med Baghdad. 011;53(3):317-9. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.533838.
8. Alfaris R, Al-Kinani KK. Preparation and Characterization of Prednisolone Acetate Microemulsion for Ophthalmic Use. J Fac Med Baghdad. 2023;65(3):205-11. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.2045.
9. Micallef J, Soeiro T, Jonville-Bera A-P, of Pharmacology FS. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pharmacology, and COVID-19 infection. Therapies. 2020;75(4):355-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.therap.2020.05.003.
10. Schechter BA. Use of topical Bromfenac for treating ocular pain and inflammation beyond cataract surgery: a review of published studies. Clinical Ophthalmology. 2019:1439-60. https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S208700.
11. Erichsen JH, Forman JL, Holm LM, Kessel L. Effect of anti-inflammatory regimen on early postoperative inflammation after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2021;47(3):323-30. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.jcrs.0000000000000455.
12. Saade JS, Istambouli R, AbdulAal M, Antonios R, Hamam RN. Bromfenac 0.09% for the treatment of macular edema secondary to noninfectious uveitis. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2021;28(2):98. https://doi.org/10.4103/meajo.meajo_134_21.
13. Kashiwagi K, Tsukahara S. Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ophthalmic solution on intraocular pressure reduction by latanoprost. British journal of ophthalmology. 2003;87(3):297-301. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.87.3.297.
14. Hoffman RS, Braga-Mele R, Donaldson K, Emerick G, Henderson B, Kahook M, et al. Cataract surgery and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery. 2016;42(9):1368-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrs.2016.06.006.
15. Issa S, Pacheco J, Mahmood U, Nolan J, Beatty S. A novel index for predicting intraocular pressure reduction following cataract surgery. British journal of ophthalmology. 2005;89(5):543-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2004.047662.
16. Tobimatsu Y, Ogihara R, Endo N, Hirose A, Takeda R, Babazono T, et al. Comparison of the Effect of Bromfenac versus Betamethasone Ophthalmic Solutions in Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema. Current Eye Research. 2023;48(1):80-5. https://doi.org/10.1080/02713683.2022.2140438.
17. Su T-Y, Ting P-J, Chang S-W, Chen D-Y. Superficial punctate keratitis grading for dry eye screening using deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Sensors Journal. 2019;20(3):1672-8. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2019.2948576.
18. Al-Quriashi NK, Essa SO. 0.1 Second versus 0.2 Second pulse duration of Frequency Doubled Nd: YAG Laser in treatment of Clinically Significant Diabetic Maculopathy. J Fac Med Baghdad. 2009;51(1):112-5. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.5111196.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Enas S. Abdullah, Samara M. Ali, Zaid R. Hussein

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


