Taste Masking Techniques of Unpleasant Drugs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad2164الكلمات المفتاحية:
ألطعم ألمر, تقبل ألمريض, حجب ألطعمالملخص
ألخلفية: حجب ألطعم هو تقليل للطعم غير ألمرغوب به للمركبات ألعضويه داخل ألتجويف ألفمي.
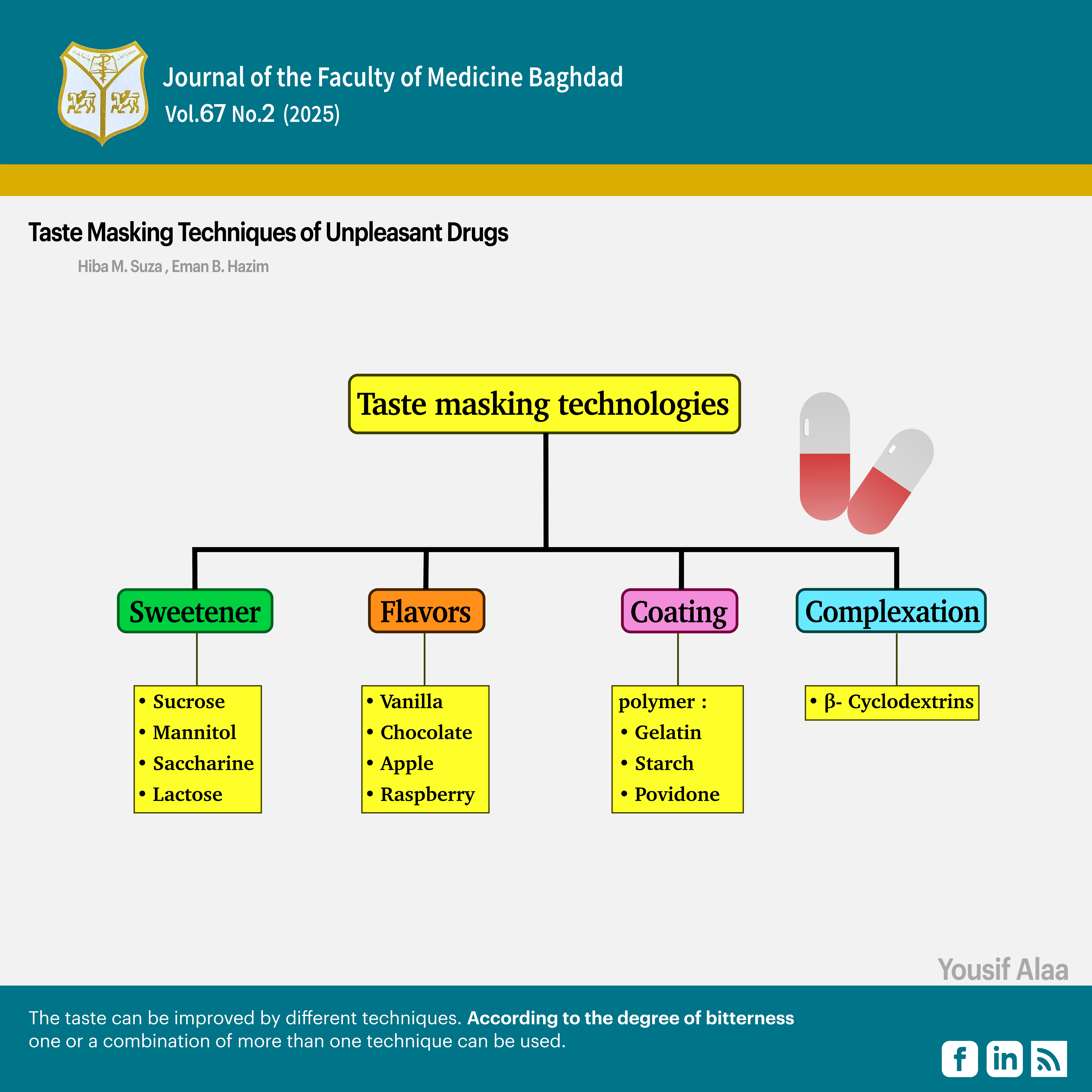
ألهدف: لتسليط الضوء على أهمية حجب الطعم, العوامل المؤثرة عليه, طرق تحضيره و تقييمه خارج وداخل الجسم.
ألنتائج: تكمن أهمية حجب ألطعم غير ألمرغوب به في تحسيين تقبل ألمريض لأخذ ألدواء خاصة لمرضى ألاطفال وكبار ألسن وبالتالي تحسين الفعالية ألدوائية.
ألأستنتاج: يمكن حجب ألطعم غير ألمرغوب به بعدة طرقوذلك اعتمادآ على درجة ألمرارة للدواء يمكن أستخدام طريقة واحدة أو ألحاجة ألى مزج أكثر من طريقة.
التنزيلات
المراجع
1. Sawan M. S. Review on taste masking approaches in oral pharmaceutical dosage forms. LM Jo. 2015;1: 33-43. https://ijprajournal.com/issue_dcp/Review%20on%20Taste%20Masking%20Approaches%20and%20Evaluations.pdf.
2. Deepak S, Dinesh K, Mankaran S, Gurmeet S, Singh R. Taste masking technologies: a novel approach for the improvement of organoleptic property of pharmaceutical active substance. Int Res J Pharm. 2012;3(4):108-16. https://irjponline.org/index.php/irjp/article/view/2148.
3. Fating H, Ambadkar J, Kajale A. Advances in taste masking of drug: a review study. Jddt. 2022; 12(3-S):262-267. https://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v12i3-S.5442
4. Gvozdeva Y. Taste masking of bitter drugs for incorporation into orodispersible tablets. Ijprajournal. 2021; 6(6): 120- 126. https://doi.org/110.35629/7781-0606120126.
5. Witt M, Reutter K. Anatomy of the tongue and taste buds. Handb olfaction gustation third Ed. 2015;(1851):637-664. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118971758.ch29.
6. Tripathi A, Parmar D, Patel U, Patel G, Daslaniya D, Bhimani B. Taste masking: A novel approach for Bitter and obnoxious drugs. J Pharm Sci Biosci Res. 2011;1(3):136-142. https://www.pharmaexcipients.com/wp-content/uploads/attachments/2_1146.pdf?t=1453801170.
7. Sharma S, Lewis S. Taste masking technologies: A review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2010;2(2):6-13. https://innovareacademics.in/journal/ijpps/Vol2Issue2/408R.pdf.
8. Abraham J, Mathew F. Taste masking of peadiatric formulation: A review on technologies, recent trends and regulatory aspects. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014;6(1):12-9. https://innovareacademics.in/journal/ijpps/Vol6Issue1/7873.pdf.
9. Vinod S, Saiffee M, Shinde N, Hawaldar A, Pawar N. An update of taste masking methods and evaluation techniques. Der Pharm Lett. 2010;2(6):1-15. https://www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com/articles/an-update-of-taste-masking-methods-and-evaluation-techniques.pdf.
10. Vesey C. Basic considerations for taste masking. 2018;(April).
11. Amelian A, Winnicka K. Polymers in pharmaceutical taste masking applications. Polymry. 2017; 62(6): 419- 427. https://doi.org/10.14314/polimery.2017.419.
12. Ibrahim M, Abou El Ela A. Optimized furosemide taste masked orally disintegrating tablets. Saudi Pharm J. 2017;25(7):1055-62.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2017.04.002.
13. Madgulkar A, Bhalekar M, Vaidya A, Kaushal P, Mudalwadkar R. Development of hot melt coating technique for taste masking of chloroquine phosphate tablets. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2019;9(4-s):562-568. https://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v9i4-s.3213.
14. Munira M, Sudha R, Swapan K. Taste masking techniques for bitter drugs_ an oerview . Int J Pharm Technol. 2012;4(2):2100- 2118. https://www.ijnrd.org/papers/IJNRD2406442.pdf.
15. Dungarwal U, Patil S. Development of orodispersible tablets of taste masked rizatriptan benzoate using hydroxypropyl β cyclodextrin. J Pharm Investig. 2016;46(6):537-545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0240-5.
16. Liu T, Wan X, Luo Z, Liu C, Quan P, Cun D, et al. A donepezil/cyclodextrin complexation orodispersible film: Effect of cyclodextrin on taste-masking based on dynamic process and in vivo drug absorption. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2019;14(2):183- 192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2018.05.001.
17. Anuradha K, Adarsh K, Mishra M, Maqbool A, Pathak S, Biswal P. Various approaches towards taste masking : An overview. ijprajournal. 2018; 2(4): 1-9.
18. Panraksa P, Boonsermsukcharoen K, Hwang K, Park E, Jantrawut P. Taste masking of nizatidine using ion-exchange resins. Processes. 2019;7(11): 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110779.
19. Alaqarbeh M. Adsorption phenomena : definition , mechanisms , and adsorption types : short review. Rhazes: RHAZES GAC journal. 2021; 13: 43-51. https://doi.org/10.48419/IMIST.PRSM/rhazes-v13.28283.
20. Gupta P, Tiwari A, Mishra MK. Taste masking of drugs: an extended approach. Int J Curr Adv Res. 2017;6(3):2571-2578. https://doi.org/10.24327/ijcar.2017.2578.0051.
21. Sona P, Muthulingam C. Formulation and evaluation of taste masked Orally disitegrating tablets of diclofenac sodium. Int J PharmTech Res. 2011;3(2):819-26.
22. Shet N, Vaidya I. Taste masking: A pathfinder for bitter drugs. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2013;18(2):1-12.
https://www.globalresearchonline.net/journalcontents/v18-2/01.pdf.
23. Forster S, Lebo D. Continuous melt granulation for taste-masking of ibuprofen. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(6): 1-20. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060863.
24. Vummaneni V, Nagpal D. Taste masking technologies : An overview and recent updates. Int J Res Pharm Biomed Sci. 2012;3(2):510-524.
25. Iftikhar B, Liaqat R. Taste masking practices in solid form drugs. Journal of chimstry. 2021; 10(9): 1-7. https://www.rroij.com/open-access/taste-masking-practices-in-solid-form-drugs.pdf
26. Han C, Kim S, Oh D, Yoon J, Park E, Rhee Y, et al. Preparation, characterization, and stability evaluation of taste-masking Lacosamide microparticles. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(6): 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12061000.
27. Nikam V, Shete S, Khapare J. Most promising solid dispersion technique of oral dispersible tablet. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 2020;9(1): 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-020-00086-4.
28. Abdulqader A, Al-Khedairy E. Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving tablets of taste-masked ondansetron hydrochloride by solid dispersion. Iraqi J Pharm Sci. 2017;26(1):50-60. https://doi.org/10.31351/vol26iss1pp50-60.
29. Alalor C. Advances in the technology of taste- masking of unplesant tasting oral dosage forms: Areview. Continental J. Applied Sciences. 2015;10 (1): 18- 27. https://doi.org/10.5707/cjapplsci.2015.10.1.18.27.
30. Suza H, Al-Khedairy E. Formulation and Evaluation of Prednisolone -Loaded Alginate Beads for Taste Masking. ejhm. 2023; 90(2): 2178-2186.https://doi.org/10.21608/ejhm.2023.285683.
31. Lu H, Butler J, Britten N, Venkatraman P, Rahatekar S. Natural antimicrobial nano composite fibres manufactured from a combination of alginate and oregano essential oil. Nanomaterials. 2021;11(8):1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082062.
32. Naranjo A, Quintero J, Rojaso J, Ciro G. Modified-release of encapsulated bioactive compounds from annatto seeds produced by optimized ionic gelation techniques. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80119-1.
33. Leong J, Lam W, Ho K, Lim H, Voo W, Lee M, et al. Advances in fabricating spherical alginate hydrogels with controlled particle designs by ionotropic gelation as encapsulation systems. Particuology . 2016; 24:44-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2015.09.004.
34. Shivhare UD, Mathur VB, Shrivastava CG, Ramteke VI. Preparation of microbeads by different techniques and study of their influence on evaluation parameters. J Adv Pharm Educ Res. 2013;3(3):279-288. https://japer.in/storage/models/article/3bPt79TvwejPZ6yyvGGvMXKNwRhU466A9Z0b7Jau61bnRvw0Dm2w4IqQrJ5i/preparation-of-microbeads-by-different-techniques-and-study-of-their-influence-on-evaluation-param.pdf.
35. Rajmohan D, Bellmer D. Characterization of spirulina-alginate beads formed using ionic gelation. Int J Food Sci. 2019;2019: 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7101279.
36. Sutriyo, Iswandana R, Fauzi F. Strategy to mask the bitter taste of momordica charantia extract using alginate-gelatin beads. Int J Appl Pharm. 2018;10(S- 1):381-383. https://doi.org/10.22159/ijap.2018.v10s1.84.
37. Toor R, Kumari B. New technologies in the formulation of oral dispersible tablets and taste masking: a review. Indian Res J Pharm Sci. 2018;5(1):1288-1301. https://doi.org/10.21276/irjps.2018.5.1.7.
38. Sriram P, Suttee A, Marasakatla Z. Formulation and taste masking of metronidazole oral disintegrating tablets by a novel approach. Int J Pharm Qual Assur. 2020;11(3):399-403. https://doi.org/10.25258/ijpqa.11.3.15.
39. Kumar KPS, Bhowmik D, Srivastava S, Paswan S, Dutta a S. Taste masked suspension. The Pharma Journal. 2012;1(2):1-7.
40. Sohi H, Sultana Y, Khar RK. Taste masking technologies in oral pharmaceuticals: Recent developments and approaches. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2004;30(5):429-448. https://doi.org/10.1081/DDC-120037477.
41. Amelian A, Wasilewska K, Wesoły M, Ciosek-Skibińska P, Winnicka K. Taste-masking assessment of orally disintegrating tablets and lyophilisates with cetirizine dihydrochloride microparticles. Saudi Pharm J. 2017;25(8):1144-1150.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2017.06.001.
42. Chauhan R. Taste masking: A unique approach for bitter drugs. J Stem Cell Biol Transplant. 2017;1(2): 1-6. https://doi.org/10.21767/2575-7725.100012.
43. Malode Sarika S, Gudsoorkar Vilas R. Taste masking: overview of taste assessment approaches in the development of oral pharmaceutical formulation. iajpr. 2014;4(01): 204- 211. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344960776.
التنزيلات
منشور
إصدار
القسم
الفئات
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2025 Hiba M. Suza, Eman B. Hazim

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


