التهاب الكبد الفيروسي (أ): الملف الوبائي, السريري و حالات المرضى بعد العلاج في مستشفى حماية الاطفال التعليمي / مدينة الطب و ضرورة وضع برنامج لقاحي له.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad2410الكلمات المفتاحية:
مفتاح الكلمات: التهاب الكبد الفايروسي أ ، لقاح التهاب الكبد الفايروسي أ، لقاح التهاب الكبد الفايروسي أ، اعتلال الدماغ الكبدي، فشل الكبد الحاد، مستشفى حماية الطفل التعليميالملخص
خلفية البحث:
فايروس التهاب الكبد نوع أ هو فايروس الحمض النووي الريبي احادي الجديلة ، عشيرينيالوجوه، غير مغلف، ينتمي الى جنس ال فايروسات الكبدية من عائلة الفايروسات البيكارناوية. وينتقل بشكل رئيسي عن طريق البراز والفم. ووفقا لمنظمة الصحة العالمية، هناك حوالي١،٥مليون حالةمن التهاب الكبد نوع أ على مستوى العالم كل عام. ترتبط الظروف الاجتماعية والاقتصادية ارتباطا وثيقا بمعدلات الإصابة، قهو
مرض يمكن الوقاية منه باللقاحات. يوضح بحثنا حجم التهاب الكبد أ في المستشفى التعليمي لرعاية الأطفال/ مدينة
الطب.
الاهداف :
يهدف بحثنا الى توفير المعلومات الصحيحة والكافية لفهم الاعراض السريرية ونتائج التهاب الكبد أ في
بلدنا. والاهم من ذلك، التأكيد على الحاجة الى النظر في التدابير الوقائية المناسبة بناءا على البيانات والإحصاءات
المتاحة التي لخصناها في هذا البحث.
المرضى وطرق العمل/ المواد وطرق العمل:
أجرينا
دراسة تحليلية حشدية رجعية من الفترة كانون
٢٠١٩ الثاني/الى٢٠٢٢ / تموز/ ١٠
٢٠٢٢ / تموز/ ١١ مع دراسة حشدية مستقبلية من الفترة
الى
٢٠٢٢ /ايلول/ ٣٠
من اجل تلخيص إحصاءات حالات الإصابة بفايروس التهاب الكبد الفايروسي.تتضمن دراستنا
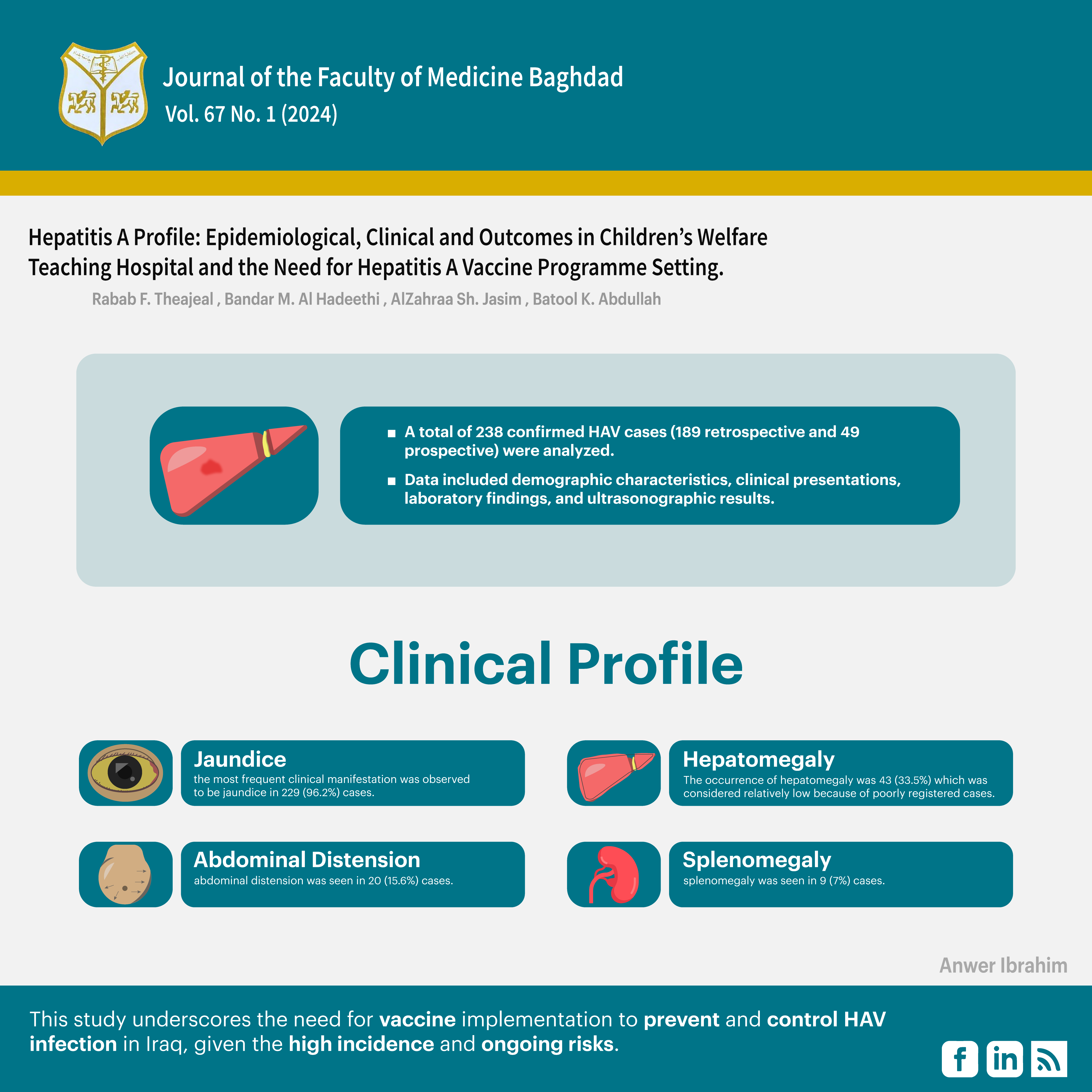
238
حالة من سجلات مستشفى حماية الطفل التعليمي. تم اجراء بحث شامل باستخدام المواقع الطبية الموثوقة
PUBMED,Google scholar, Research gate,CDC
للحصول على الدراسات الأكثر صلة لتضمينها في
مناقشتنا.
لنتائج:
اعلى نسبة اصابات هي في الفئة العمرية(١٠ - ٦ )نسبة الذكور (٥٠،٨
٪ ) بينما نسبة الاناث (٤٩،٢٪)اظهر الملف السريري الآتي:
يرقان(٩٦٫٢،٪ )، انتفاخ البطن(١٥،٦٪) تضخم الطحال (٧٪)، النزيف(٥،٩٪)،نتائج الموجات فوق الصوتية: تضخم الكبد (٤٥،٤٪)،تورم جدار المرارة(٣١،٢٪)،تضخم الطحال(١٤،٩٪)،،الاستسقاء (٤،٢٪)
- المعدل للبيانات الاتية: مصل الكلوتامك باروفك ترانسامينيز(
٧٨٦،٨- وحدة/لتر)، مصل الكلوتامك
اوكسالواستك ترانسامينيز(٦٤٧،٦٪)، اجمالي البليروبين في الدم( مجم/ذيسيلتر)، زمن للبروثرومبينأو مؤشر السيولة في الدم(١٤٫٩ ثانية) الدم زمن الثرومبوبلاستين الجزئي (٣٦٫٤٥
ثانية) النسبة المعيارية الدولية(١،١٥)
٨حالات كانت مصابة بفشل الكبد الحاد (٤وفيات) و٦ حالات مصابة باعتلال دماغي كبدي (٥وفيات)، معدل الوفاة (٢٫١ ٪) ونسبة وفاة الذكور الى الاناث هي (١:٤)
الاستنتاجات:
تؤكد نتائج هذا البحث
على الحاجة الى اجراء
مناقشات حول تطبيق اللقاح للوقاية من الإصابة
بفايروس التهاب الكبد الوبائي أ ومكافحته في العراق حيث نلاحظ أن الإصابات مرتفعة والمخاطر مستمرة.
مفتاح الكلمات:
التهاب الكبد الفايروسي أ ، لقاح التهاب الكبد الفايروسي أ، لقاح التهاب الكبد الفايروسي أ، اعتلال
الدماغ الكبدي، فشل الكبد الحاد، مستشفى حماية الطفل التعليمي
التنزيلات
المراجع
1. Odenwald MA, Paul S. Viral hepatitis: Past, present, and future. World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr 14;2814):1405-1429.PMID: 35582678; PMCID: PMC9048475.Hollinger FB, Liang TJ. Hepatitis B virus. Fields virology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia. 2017:2971-3036.https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1405.
2. Abutaleb A, Kottilil S. Hepatitis A: Epidemiology, Natural History, Unusual Clinical Manifestations, and Prevention. GastroenterolClin North Am. 2020 Jun;492):191-199. Epub 2020 Mar 29. PMID: 32389358;PMCID:PMC7883407.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2020.01.002.
3. Aggarwal R, Goel A. Hepatitis E: current status in India. Clin Liver Dis
Hoboken). 2021;183):168-172. https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.1040PMid:33163170 PMCid:PMC7609704
4. Pérez-Sautu U, Costafreda MI, Caylà J, Tortajada C, Lite J, Bosch A, Pintó RM. Hepatitis a virus vaccine escape variants and potential new serotype emergence. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011 Apr;174):734-7. Https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1704.101169. PMID: 21470474; PMCID: PMC3377408.
5. Nelson NP, Weng MK, Hofmeister MG, Moore KL, Doshani M, Kamili S, Koneru A, Byrd KK. Prevention of hepatitis A through active or passive immunization: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2020. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2020;69No. RR-5):1-38. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6905a1.
PMid:32614811 PMCid:PMC8631741
6. Gabrielli F, Alberti F, Russo C, Cursaro C, Seferi H, Margotti M, Andreone P. Treatment Options for Hepatitis A and E: A Non-Systematic Review. Viruses. 2023 Apr 28;155):1080. Https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051080. PMID: 37243166; PMCID: PMC10221699.
7. UFallucca A, Restivo V, Sgariglia MC, Roveta M, Trucchi C. Hepatitis a Vaccine as Opportunity of Primary Prevention for Food Handlers: A Narrative Review. Vaccines Basel). 2023 Jul 21;117):1271. Https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071271. PMID: 37515087; PMCID: PMC10383099.
8. Dhawan A, Cheeseman P, Mieli-Vergani G. Approaches to acute liver failure in children. Pediatr Transplant. 2020;244):e13678.https://doi.org/10.1111/petr.13678 PMid:32343885
Castaneda D, Gonzalez AJ, Alomari M, Tandon K, Zervos XB. From hepatitis A to E: A critical review of viral hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Apr 28;2716):1691-1715. Https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i16.1691. PMID: 33967551; PMCID: PMC8072198.
9. Migueres M, Lhomme S, Izopet J. Hepatitis A: Epidemiology, High-Risk Groups, Prevention and Research on Antiviral Treatment. Viruses. 2021;1310):1900. doi:10.3390/v13101900 https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101900
PMid:34696330 PMCid:PMC8540458
10. Langan RC, Goodbred AJ. Hepatitis A. Am Fam Physician. 2021 Oct 1;1044):368-374. PMID: 34652109.
11. Zhang L. Hepatitis A vaccination. Hum VaccinImmunother. 2020 Jul 2;167):1565-1573. Epub 2020 Jul 10. PMID: 32649265; PMCID: PMC7482852.https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2020.1769389
12. Abu-Raddad LJ, Ayoub HH, Chemaitelly H, Mumtaz GR, Butt AA, May MT, Hallett TB. Characterizing the Epidemiology of Hepatitis A in the Middle East and North Africa: Implications for Vaccination Strategies. Journal of Infection and Public Health. 2021;144):409-420.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2021.01.002PMid:33743368PMCid:PMC7834000
13. Badur S, Öztürk S, Ozakay A, Khalaf M, Saha D, Van Damme P. A review of the experience of childhood hepatitis A vaccination in Saudi Arabia and Turkey: implications for hepatitis A control and prevention in the Middle East and North African region. Human Vaccines &Immunotherapeutics. 2021 Oct 3;1710):3710- 28. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2021.1920871
PMid:34213403 PMCid:PMC8437515
14. Foster MA, Hofmeister MG, Xing J, et al. Declining hepatitis A mortality in the United States during the era of hepatitis A vaccination. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2021;2239):1450-1459. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab046
PMid:35238363 PMCid:PMC8892529
15. Chicago Department of Public Health. Hepatitis A Response and Immunization Program. *Chicago Health Reports*. 2021;Issue 7:45-50. Available at:https://www.chicagohan.org/documents/14171/93622/Hepatitis_A_10242017
16. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC). Hepatitis A Surveillance Report. *CDC Annual Reports*. 2021. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2021surveillance/hepatitis-a.htm
17. Hussein HK. Three years epidemiological study of acute hepatitis A infection in Al Elwyia pediatric teaching hospital, Baghdad, Iraq. Rawal Medical Journal. 2019 Oct 8;443):436-.
18. Daood II, RH I. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis A Virus HAV) in Mosul City. Medico Legal Update. 2020 Jan;201):310-4.
19. AA Darwish L, Nasrallah AA, Al Mousaw A. Hepatitis A in Kerbala: Eight Year Epidemiological Study. Kerbala Journal of Medicine. 2018 Jun 1;111):3873-83.
20. Akman AÖ, Burhan BY, Uzun AK, Taş D. Hepatitis A virus age-specific seroprevalence after the implementation of a Toddlers' Vaccination in Turkey: Shifting susceptibility to adolescents. Turk PediatriArs. 2020 Dec 16;554):370-375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.05.114PMID: 33414654; PMCID: PMC7750331.
21. Elsabawy MN. Hepatitis gender gap in Egypt: A study in medical geography. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2018 Jan 1;19:121-30.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.05.114.
22. Choe YJ, Son H. The changing gender differences in hepatitis a incidence in South Korea. Vaccine. 2020 Jan 22;384):712-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.11.048
PMid:31787416
23. Cao G, Jing W, Liu J, Liu M. The global trends and regional differences in incidence and mortality of hepatitis A from 1990 to 2019 and implications for its prevention. Hepatol Int. 2021 Oct;155):1068-1082.. Epub 2021 Aug 3. PMID: 34345993; PMCID: PMC8514357.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10232-4
24. Abdullah I; Goreal A. Seroprevalence of anti-hepatitis A virus antibody in Iraq. East Mediterr Health J. 2022;2811):829–834. https://doi.org/10.26719/emhj.22.087
25. Tong MJ, el-Farra NS, Grew MI. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: recent experience in a community teaching hospital. J Infect Dis. 1995 Mar;171Supplement_ 1:S15-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10232-4. PMID: 7876641.
26. Arooj S, Mukhtar MU, Abbas F. An acute viral hepatitis epidemic: does ultrasound help the pediatrician? BMC Res Notes. 2021 Mar 10;141):95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-021-05510-1. PMID: 33691769; PMCID: PMC7944630.
27. Han HS, Park CM, Lee DS, Sinn DH, Gil E. Evaluating mortality and recovery of extreme hyperbilirubinemia in critically ill patients by phasing the peak bilirubin level: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2021Aug5;168):e0255230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0255230. PMID: 34351969; PMCID: PMC8341602.
28. Jiang AA, Greenwald HS, Sheikh L, Wooten DA, Malhotra A, Schooley RT, Sweeney DA. Predictors of acute liver failure in patients with acute hepatitis A: an analysis of the 2016-2018 San Diego county hepatitis A outbreak. InOpen forum infectious-diseases 2019 Nov Vol. 6, No. 11, p. ofz467). US: Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofz467 PMid:31777757 PMCid:PMC6868431
29. Anand AC, Nandi B, Acharya SK, et al. Indian National Association for the Study of the Liver Consensus Statement on Acute Liver Failure Part 1): Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Presentation and Prognosis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2020 Jul-Aug;104):339-376. Epub 2020 Apr 28. PMID: 32655238; PMCID: PMC7335721.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2020.04.012
30. van Lennep M, Leijdekkers ML, Oors JM, Benninga MA, van Wijk MP, Singendonk MM. Clinical experience with performing esophageal function testing in children. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition. 2021 Feb1;722):226-31. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000003000
PMid:33230070 PMCid:PMC7815250
31. Hrynkiewicz R, Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej P. Etiology of viral induced acute liver failure and defensins as potential therapeutic agents in ALF treatment. Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 21;14:1153528. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1153528. PMID: 37153560; PMCID:PMC10160486.https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1153528
PMid:37153560 PMCid:PMC10160486
32. Naher B, Islam R, Ghosal S, Nahid KL. Rukunuzzaman 2021) Seroprevalence and Co-infection of Hepatitis A and Hepatitis E Viruses in children-A hospital-based study in Bangladesh. J NeonatolClinPediatr 8: 080. of.;4:2.
33. Escobedo-Meléndez G, Fierro NA, Roman S, Maldonado-González M, Zepeda-Carrillo E, Panduro A. Prevalence of hepatitis A, B and C serological markers in children from western Mexico. ANNALS of Hepatology. 2012 Mar
34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1665-268119)31024-5.
35. Kanda T, Sasaki R. Hepatitis A Infection in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Clinical Outcomes and Management. *Int J Mol Sci*. 2022;233):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031267
PMid:35163190 PMCid:PMC8836203
36. Thejeal RF, Abdulwahhab SB, Bahlol AR. Epidemiological study of hepatitis A infection, experience of children welfare teaching hospital: One-year analysis. EurAsian Journal of BioSciences. 2020 Aug 1;142): 6673-6677
37. Hofmeister MG, Xing J, Foster MA, et al. Hepatitis A person-to-person outbreaks: epidemiology, morbidity burden, and factors associated with hospitalization—multiple states, 2016–2019. J Infect Dis. 2021 Feb 1;2233):426-34. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa636
التنزيلات
منشور
إصدار
القسم
الفئات
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2025 Bandar M. Al hadeethi, AlZahraa Sh. Jasim, Batool K. Abdullah, Rabab F. Theajeal

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


